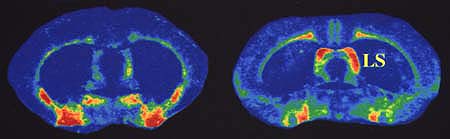
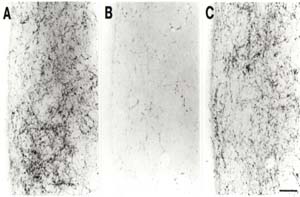
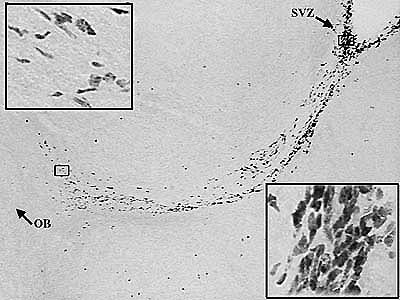
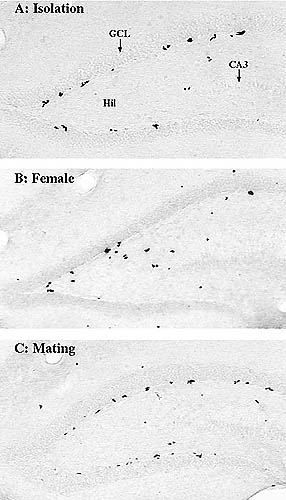
|
A male and female prairie vole |
A male prairie vole retrieves a pup |
 |
 |
|
Exposure to an unrelated male or its urinary pheromone is essential to induce estrus in female voles. |
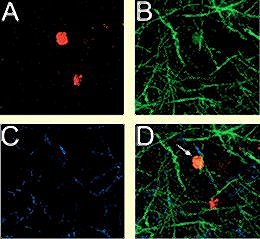
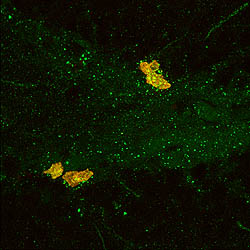
Male prairie voles become aggressive after mating and exhibit aggression towards intruders. |